Copper
Copper
Indian production of copper is not satisfactory. There are few mines of copper with low grade content. Almost all deposits of copper are of hydrothermal origin. Let's start with something which is different for copper deposits i.e. porphyry type. Although, Cu, Mo, Sn, W etc. form porphyry deposits but Cu has very large deposits of porphyry type. Do read about the world's largest copper deposit which is situated in Chile.
Copper porphyry type deposits
Characteristics of Cu porphyry deposits
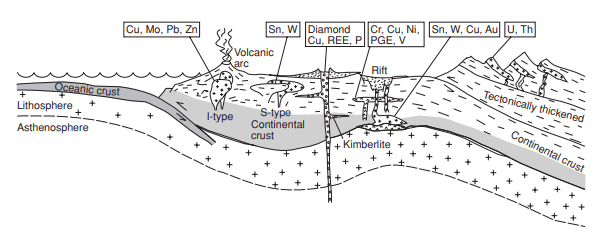
- They occurs in convergent type plate tectonics. In general, porphyry Cu–Mo deposits are associated with arc related calc–alkaline or I-type magmas.
- These are low grade and high tonnage deposits.
- These are associated with the granitic rocks and alteration zones are present with them.
- As they are associated with convergent setting, where oceanic plate is subducting, world's large deposits are present around the circ-pacific ring.
- 2 important types are present: Cu - (Mo), i.e in which Cu is dominant and other is Mo - (Cu) where Mo is dominant. Cu - (Mo) deposits form when a body of magma with a relatively low initial H2O content rise to high levels in the crust before significant crystallization takes place.
- When magma reaches the high level, vapour phase start to separates out. Here is one more interesting thing to note, Cu is compatible with crystallized matter rather than melt. But it still extracts out of magma as vapour phase has Cl ions and Cu has high affinity for these ions. They scavenge out Cu.
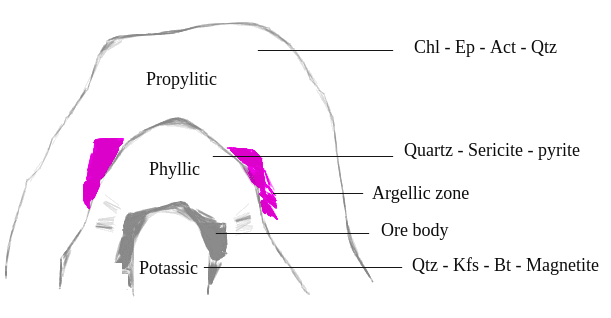
- Alteration zones associated with Cu are explained below
Potassic zone : The core alteration zone of the deposit. K - felspar, Quartz, Biotite and Magnetite are commonly present in this zone. Alunite rock is often found which is an altered product of potassic feldspar.
Phyllic zone : The common assamblage of this zone is Quartz - sericite and pyrite.
Propylitic zone : This zone possesses the assemblage of greenschist facies. Chlorite - epidote - actinolite - calcite - quartz are common minerals.
Plus, there are two more zones. An ore body zone at the boundary of potassic and phyllic, where abundant ore mineral is present. Second is argillic zone, marked in pink in the illustration, where argillic rocks are present.
Common minerals of Copper
Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2)

| Crystal system | Tetragonal |
| Colour | Brass yellow to greenish black |
| Hardness | 3.5 - 4 |
| Streak | Green tinged black (diagnostic) |
| Luster | Metallic |
Chalcopyrite can be easily confused with pyrite as both have brass yellow colour. Hardness can be used to distinguish them.
In thin section, chalcopyrite is similar to pyrrhotite.
Chalcocite (Cu2S)
| Crystal system | Monoclinic |
| Color | Gray to Black |
| Hardness | 2.5 - 3 |
| Streak | gray to black |
| Luster | Metallic |
Bornite - It's aka peacock ore mineral due to it's colour.
Carbonates
Malachite (Cu2(CO3)(OH)2) -- greenish colour rock, found in oxide zone of supergene deposit.
Azurite (Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2) -- bluish colour rock. Its also found in oxide zone of supergene deposit.
Azurite (Cu3(CO3)2(OH)2) -- bluish colour rock. Its also found in oxide zone of supergene deposit.
INDIAN DEPOSITS

Khetri copper belt, Delhi-Aravalli fold belt
Location : Khetri town is near to the Jaipur, Rajasthan. The mine is underground. Near mining area are Kho Dariba, Saladipura and Pipela.
Host rock and mineralization : Copper deposits in this area occurs in stringers, mineralized veins, fractures and along shear planes. They are believed to be formed by Erinpura granite intrusion and the mineralization is mostly confined to the Ajabgarh group (Delhi Supergroup). Host rocks are phyllite and schist.
Minerals : Chalcopyrite and Bornite are the common minerals. Pyrite, lead and zinc also present.
Age : Neoproterozoic
Singhbhum copper deposits, Singhbhum craton
Location : It extends from the Duarpuram through Dalmipuram to Baharogora. The mine extends along the shear zone includes Mosabani, Pithoragarh, Badia, Dhobani and Surda mines.
Host rock and Mineralization : The veins and lodes of Cu occurs in the Soda granite, quartzites and schists. They are believed to be formed by singhbhum granite. Deposits are confined to the shear zone.
Minerals : Chalcopyrite, pyrite and pyrrhotite are the common minerals.
Malanjhkhand copper deposits, Bastar craton
Location : This deposit is situated in the Balaghat district, Malanjhkhand, Madhya Pradesh.
Host rock and Mineralization : This deposit is Cu- Mo porphyry deposit. Copper is abundant while molybdenum is present in low quantity. The deposits was formed due to Malanjhkhand granite. The deposit has been exposed to the weathering and thus resulted in supergene enrichment.
Minerals : Chalcopyrite veins in quartz veins. Molybdenum is secondary mineral.
Age : Paleoproterozoic
Agnigundala copper deposits
These deposits are located in Cuddapah basin. The mineralization is chiefly in quartzites and dolomites in the form of stringers and veins. The chief minerals are galena and chalcopyrite.
Rangpo deposits of Sikkim
-------deposit exhausted-------




Post a Comment