Uranium
Uranium
Common Uranium minerals are
Autunite—Ca(UO 2)(PO 4 ) 2 10-12(H 2O)
Carnotite—K 2(UO 2 ) 2(VO) 4 3(H 2O)
Tyuyamunite—Ca(UO 2 ) 2(VO 4 ) 2 5- 8H 2 O
Uraninite—UO 2
Uranophane—Ca(UO 2 ) 2SiO 3(OH) 2 5(H 2O)
Uranium deposits can be primary or secondary type. Primary deposits of Uranium form directly by the magma and are categorised in two types viz. Intrusive related and IOCG type. Copper and Uranium mineralisation of Singhbhum craton is of IOCG type.
Secondary deposits of Uranium form on the basic principle that oxidized running water dissolves uranium and precipitate it when it get reduced (for eg. when it interacts with organic matter or limestone).
IOGC deposits
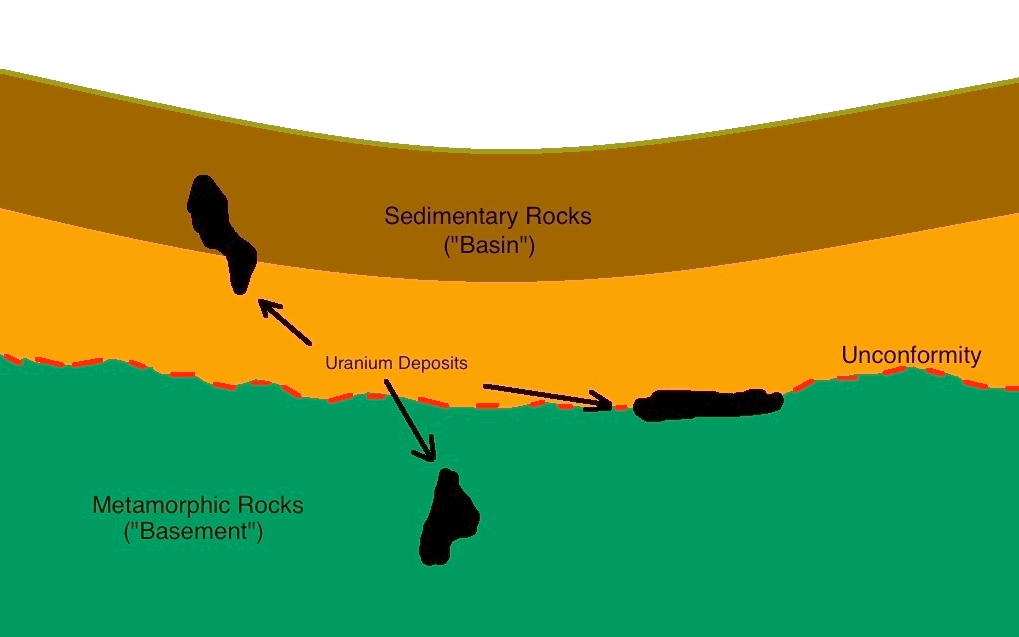
This type of deposits have been formed by magmatic processes. The host rock is mainly granitic but can range to the mafic. For best information about Uranium geology click here.UNCONFORMITY-RELATED URANIUM DEPOSITS
- As the principle indicated above, there can be different conditions above and below the unconformity. So when water containing Ur flows from oxidized to reduced condition seperated by an unconformity, it precipitates the Ur near the uncorfmity.
- Pitchblende/uraninite fills extensional features in reactivated fault zones and replaces matrix in sandstone.
- Mined by conventional methods.
Uranium precipitated under reducing conditions caused by a variety of reducing agents within the sandstone
- carbonaceous material (detrital plant debris, amorphous humate, marine algae)
- Sulfides (pyrite, H2S)
- hydrocarbons (petroleum)
- interbedded basic volcanics with abundant ferromagnesian minerals (eg chlorite)
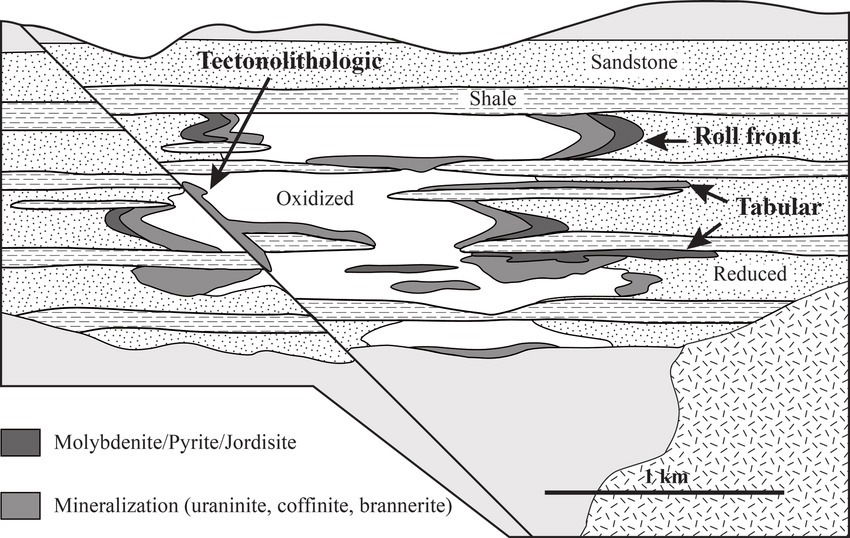
Sandstone related Ur deposits are of two types
Tabular Sandstone deposits
- Their genesis cause is exact of that principle i.e. due to reduction in the state of water.
- The mineralized zones are oriented parallel to the groundwater flow direction where it precipitated uranium. It commonly occurs with the organic debris or pyrite.
- These bodies follows palaeochannels or other depositional trends.
- These tabular uranium bodies may or may not cross the beds of sandstone in which they form.
Roll front deposits
- They are the economically most important type of sandstone hosted deposits.
- Groundwater flows in the sandstone and dissolves the Uranium which is already present in sandstone. When this flowing water encounter reduce state, such as organic matter or sulphides in the sandstone, it precipitates the uranium.
- Uranium forms irregular crescent shaped deposits and hence named roll front deposits.
- Uraninite is usual mineral. Deposits are dark, brown or black in colour.
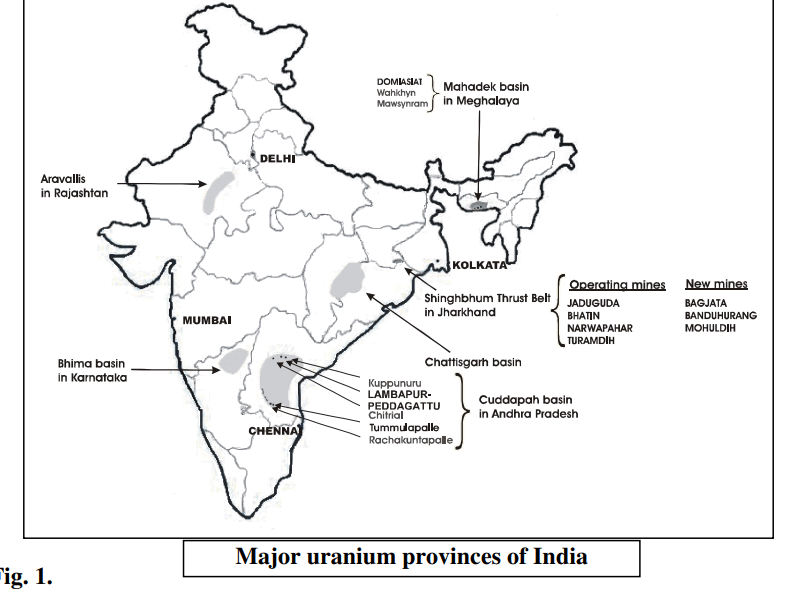
INDIAN DEPOSITS
Location: Jaduguda, Bhatin, Nawarapahar and Turamdih (map) are operational mines. Some other new mines are also developed. These are in the states of Jharkhand and Orissa.
Mineralization: There are two main ore minerals of uranium viz. Pitchblend and Uraninite. In these areas, Uraninite content is more than the pitchblend. These are of paleoproterozoic age. The mineralization is occurred mostly confined to the Singhbhum Shear Zone. These are believed to be of magmatic type deposits and soda granite is possibly responsible for this.
AGE: Paleoproterozoic
Lamabapur area is rich in uranium deposits and are of unconformity type. Mineralization occurs between the underlying granite and overlying quartzites.
Tumalapalle is a new prospected area, here the deposits are in calcareous rocks.




Post a Comment